Alternaria leaf spot, caused by the fungus Alternaria cucumerina, is a significant disease of cucumber and other cucurbit crops. While it primarily affects the foliage, severe infections can lead to defoliation, reduced yields, and diminished fruit quality due to sunscald. This disease thrives in warm, humid conditions, making it prevalent in regions with high temperatures and frequent rainfall. Understanding its symptoms, lifecycle, and impact is essential for effective management.
Symptoms
Initial Signs:
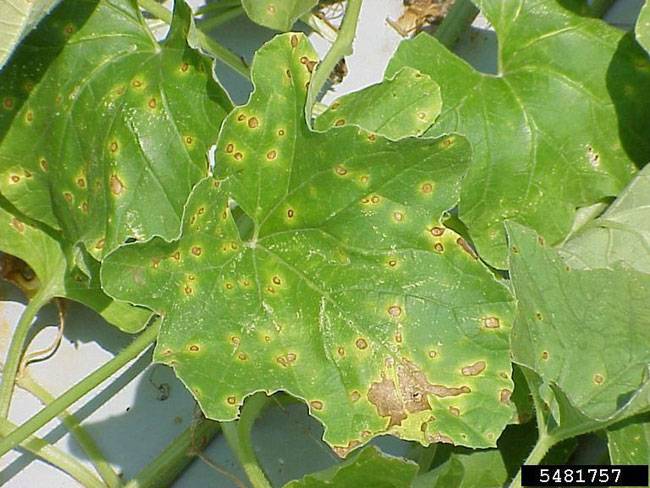
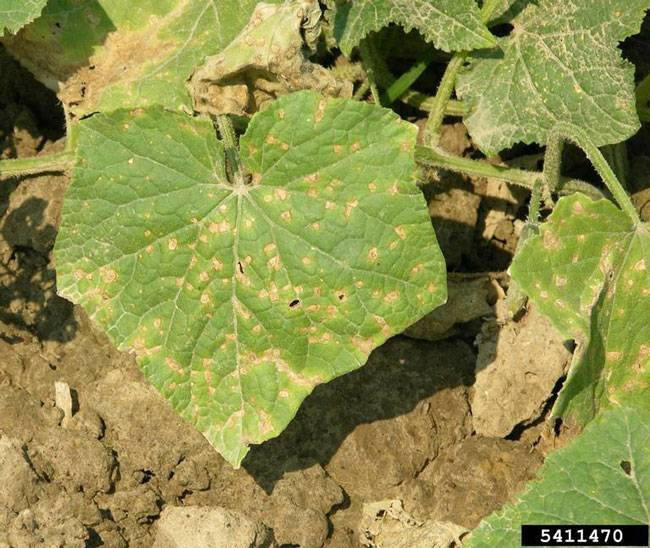
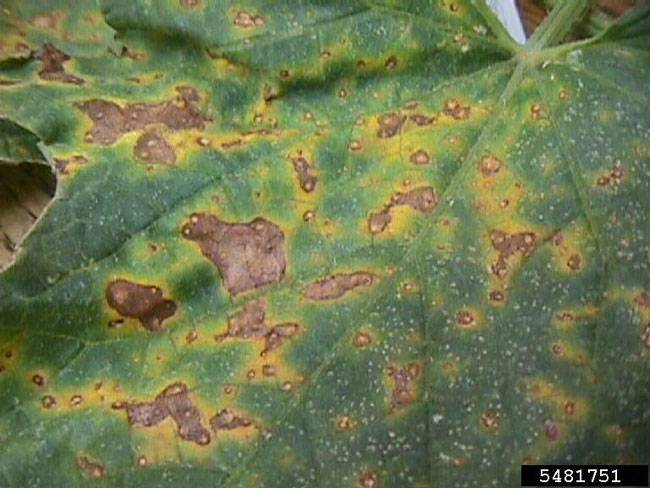
- Small, yellow-brown spots with green or yellow halos appear on the oldest leaves.
- Spots are initially water-soaked and surrounded by a greasy appearance due to cell breakdown.
Disease Progression:
- Lesions enlarge into large necrotic patches with concentric rings, giving a "target-like" appearance.
- Affected leaves curl, become brittle, and eventually die.
Impact on Plants:
- Defoliation occurs, exposing fruits to sunscald, which reduces their quality.
- Fruits may develop sunken, green-black spots if infection spreads, leading to internal decay during storage or transit.
Other Considerations:
- Alternaria leaf spots often coexist with other diseases like gummy stem blight and downy mildew, requiring careful diagnosis.
Cause and Disease Lifecycle
- Causal Agent: Alternaria cucumerina is the fungus responsible for this disease.
- Lifecycle:
- The fungus survives for up to two years in diseased plant debris.
- Conidia (spores) spread through wind and rain splash, initiating secondary infections under favorable conditions.
- Germination occurs within hours of leaf wetness, producing new spores in 3–12 days.
- Optimal Conditions:
- Temperature: 20–32°C, with nighttime temperatures around 20°C being ideal.
- Moisture: High humidity, frequent rainfall, and prolonged leaf wetness (10–24 hours) promote infection.
Crop Injury
- Impact on Leaves:
- Lesions coalesce, causing leaves to curl and die prematurely.
- Older, nutrient-deficient, or stressed plants are more susceptible.
- Impact on Fruits:
- Defoliation exposes fruits to sunburn.
- Overripe and sunscalded fruits are prone to infection, developing sunken, green-black spots with potential internal decay.
Management Recommendations
Cultural Practices:
- Remove and destroy infected plant debris to minimize fungal survival.
- Ensure proper plant spacing to improve airflow and reduce leaf wetness.
- Maintain optimal soil pH (6.0–6.5) and nutrient levels, especially nitrogen.
Environmental Adjustments:
- Avoid overhead irrigation to limit leaf wetness.
- Monitor and reduce periods of prolonged humidity, if possible.
Chemical Controls:
- Use fungicides as a preventive measure during high-risk periods.
Alternaria leaf spot of cucumber is a manageable disease if detected early and addressed promptly. By adopting an integrated approach that combines cultural practices, environmental management, and chemical control, farmers can protect their crops from severe losses. Ensuring proper diagnosis and timely intervention is key to sustaining high-quality yields in cucurbit cultivation.